It is estimated that in 2025 ~ 60% of ransomware attacks will contain some level of AI at their core. The financial and operational impact of these attacks will continue to escalate. Industries impacted will include manufacturing, automotive, telecommunications, utilities, oil and gas, and healthcare. Malicious actors are continuously developing new tools and methodologies, and AI is now taking center stage in that arsenal.
Hackers are increasingly using AI to enhance the efficiency, stealth, and impact of ransomware attacks. Here’s how they’re doing it:
Faster and More Accurate Network Scanning & Targeting
- Automated reconnaissance: AI helps identify vulnerabilities in networks more efficiently, scanning for weaknesses and prioritizing high-value, high-impact, targets.
- Target selection: Machine learning analyzes network and user data to find targets likely to pay a ransom, such as organizations that produce highly sensitive data and/or that exhibit weak security postures.
Adaptive Malware Behavior
- Polymorphic ransomware: AI helps ransomware mutate its code to avoid detection by signature-based antivirus solutions.
- Evasive techniques: AI allows ransomware to learn from detection attempts and adapt its behavior in real-time (e.g., delaying execution, mimicking normal user behavior).
- Automatically adjusts obfuscation strategies based on detection attempts
- Uses AI to select which encryption or packing methods work best
- Modifies payload delivery techniques depending on the target’s detection capabilities
Intelligent Brute Forcing and Password Cracking
- Machine learning models can improve password-guessing success rates by understanding common patterns and user behaviors.
- AI agents learn over time which cracking strategies are most effective
- Make a password guess, get feedback (was it right or wrong?), and optimize future guesses.
Smarter Phishing and Social Engineering
- AI-generated emails: Attackers use large language models (LLMs) to craft highly convincing, personalized phishing emails that bypass traditional security filters.
- Voice and video deepfakes: AI is used to clone voices or even create synthetic videos to impersonate executives or trusted contacts.
Optimized Data Exfiltration and Analysis
- AI models analyze hijacked data to extract the most sensitive or valuable information quickly, creating leverage that makes extortion attempts more impactful.
- Evasion techniques: AI models adaptively avoid detection by intrusion detection systems (IDS) or antivirus software by mimicking normal user behavior or altering traffic patterns.
- Insider threat modeling: AI can be trained to predict the best time and method to extract data by analyzing user behavior and system logs.
- Stealthy automation: AI-driven bots or scripts automatically locate, package, and transmit sensitive files while minimizing detection risk by mimicking legitimate processes.
Deepfake Threats in Double Extortion
- In double extortion scenarios, hackers threaten to release not only stolen data but also deepfake content (e.g., fake videos of executives), adding psychological pressure.
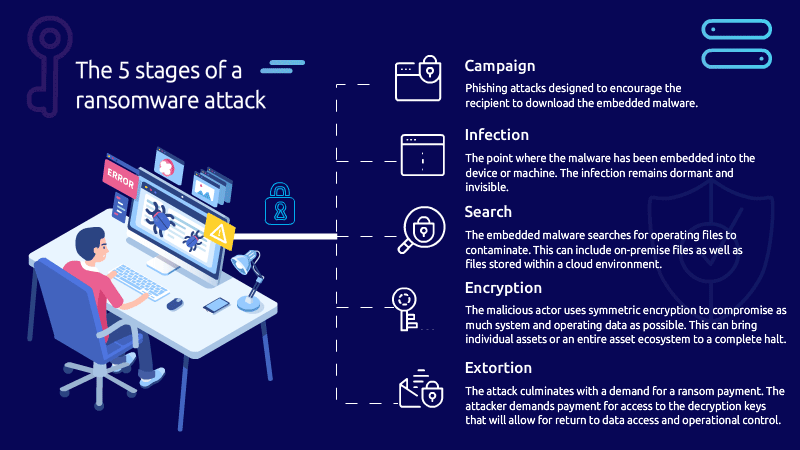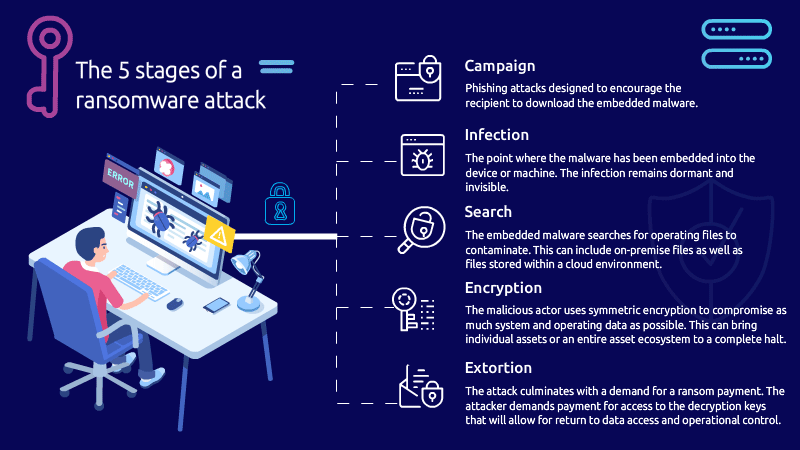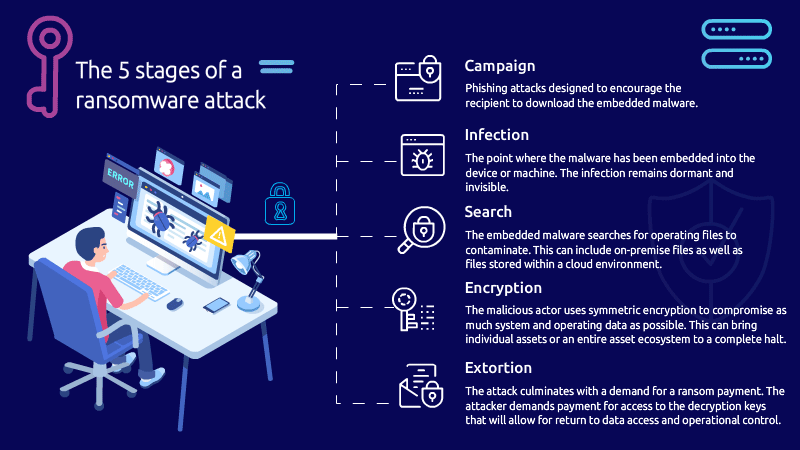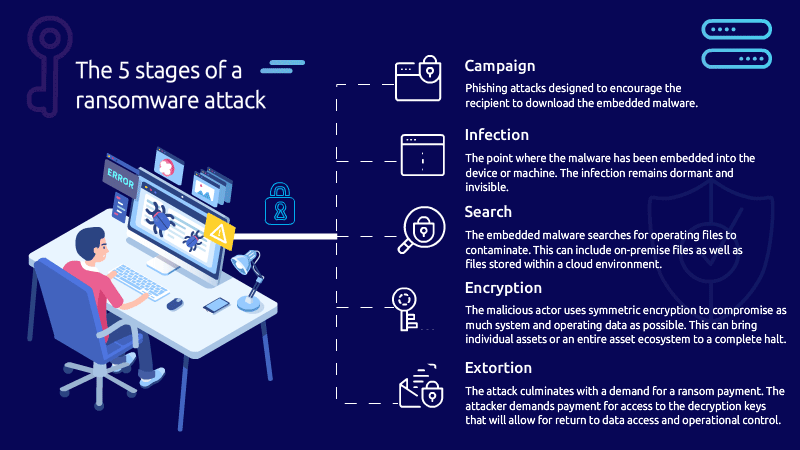
The use of AI in ransomware dramatically raises the stakes for cybersecurity, requiring more advanced, adaptive defenses and greater emphasis on threat intelligence, anomaly detection, and incident response. As AI tools become more accessible, the potential for their misuse by cybercriminals grows, posing a significant challenge for governments, organizations, and individuals.
Visit Ransomware Protection to get started on protecting your operation from AI-enabled ransomware attack.
