The accelerated growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the expanding use of edge computing have introduced new challenges for cybersecurity. Edge devices, which refer to computing devices located closer to the source of data generation, are now integral components within every industry sector, including manufacturing, telecommunications, energy, and automotive. However, as the demand for faster processing and real-time data analysis continues to surge, maintaining edge device security has become increasingly complex.
Edge Devices Defined
Edge devices are physical entities that perform computational tasks close to where the data is generated, rather than relying on a centralized cloud-based system. These devices range from smart sensors, wearables, and industrial machines, to autonomous vehicles and smart home systems. Edge computing allows for faster decision-making and reduces the need to transmit massive amounts of data to the cloud. In many cases, edge devices are designed to be lightweight, energy-efficient, and often operate autonomously without direct human intervention.
The Edge Device Security Challenge
The inherent advantages of edge devices are immense; however, their security vulnerabilities present a host of challenges, including the following:
- Increased attack surfaces: The proliferation of connected edge devices leads to an expanded attack surface. Each device can potentially become a target for cybercriminals, especially when devices are dispersed across large, decentralized networks in remote locations.
- Weak security protocols: Many edge devices, especially those with limited processing power, are not equipped with sophisticated security protocols. This makes them attractive targets for attackers who exploit weak authentication, encryption, and other security vulnerabilities.
- Data privacy: Since edge devices often collect sensitive information in real time, they are prime targets for data breaches. If data is not properly encrypted or protected, there is a risk of it being intercepted, manipulated, or stolen by malicious actors.
- Complexity of updates and patches: Edge devices are often difficult to update remotely due to their distributed nature. Without proper patch management, these devices may remain vulnerable to known exploits for extended periods, increasing the risk of attacks.
- Limited Security Resources: Many edge devices are resource-constrained and cannot support advanced security technologies such as real-time monitoring, intrusion detection systems, or firewalls. This limitation makes it more difficult to safeguard these devices from cyber threats.
AI-Enabled Edge Device Security
AI will play an increasingly crucial role in enhancing edge device security. AI’s contributions will include the following:
- Proactive threat detection
- AI-powered models analyze network traffic and system behavior to detect unusual activities in real time. Machine learning algorithms identify anomalous behavior and flag potential breaches. This enables transition from a reactive to a proactive security footing.
- Real-time malware and phishing detection
- Self-learning AI models continuously scan for malware signatures and phishing attempts throughout the entire security kill chain. The models self-improve over time, enhancing their ability to detect zero-day exploits and advanced persistent threats (APTs).
- Intrusion prevention
- AI-driven intrusion detection systems (IDS) can recognize, in real time, malicious activities such as unauthorized access or malware injection. AI-enabled security enhances existing signature-based and behavior-based threat detection abilities to either prevent an attack or to substantially mitigate its spread and damage.
- Automated, insight-fueled, response
- AI models autonomously respond to threats by isolating compromised devices, shutting down malicious processes, and enforcing security policies. Adaptive security mechanisms enable edge devices to dynamically react to threats and breaches.
- Security policy enforcement
- AI-enabled edge device security ensures compliance with security policies by enforcing encryption, authentication, and data protection rules. It also helps organizations adhere to regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and NIST.
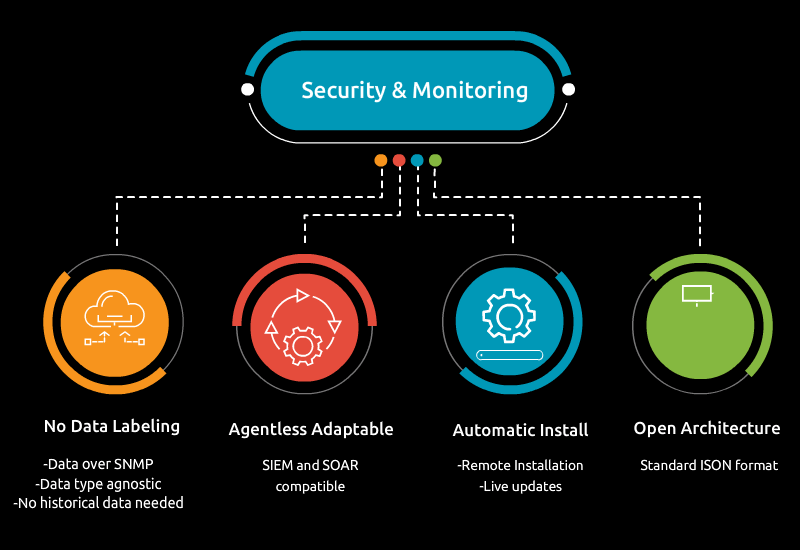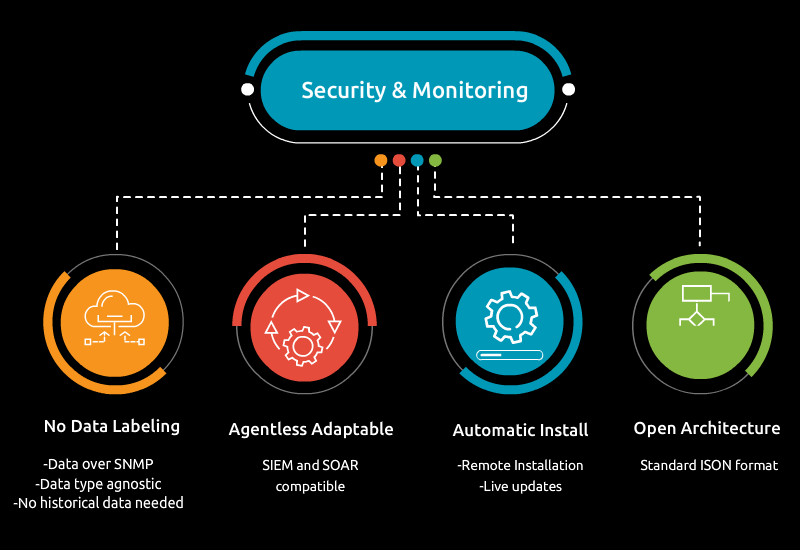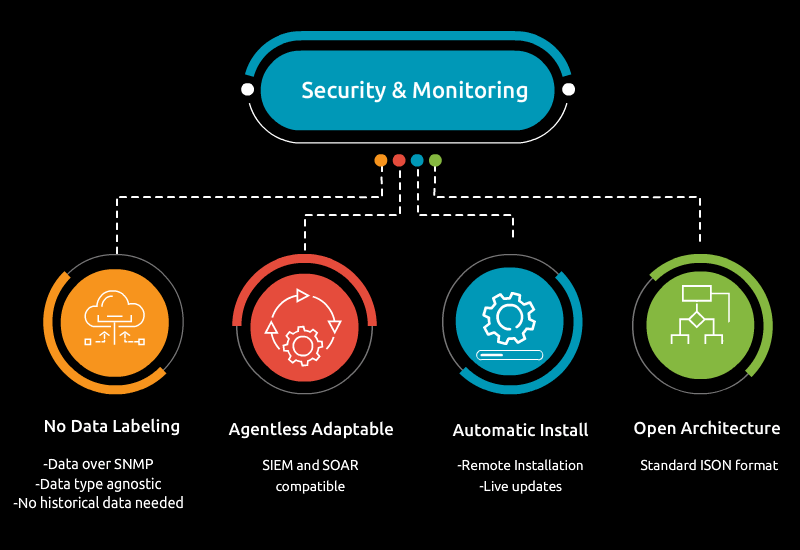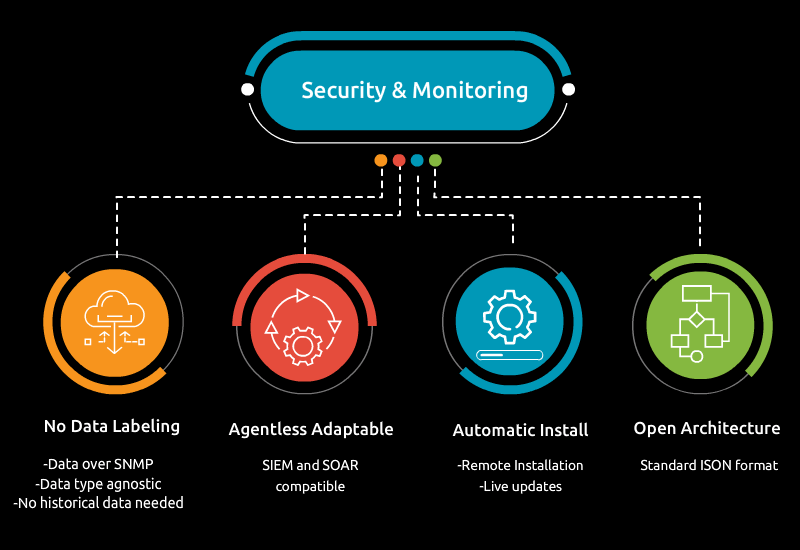
Edge devices are revolutionizing industries by enabling real-time data processing, reducing latency, and increasing efficiency. However, their rapid growth also introduces significant cybersecurity challenges. To ensure robust edge device security, a multi-faceted approach that includes strong authentication, encryption, regular updates, and intelligent monitoring is essential. By taking a proactive approach to security, operations can confidently deploy edge devices while minimizing the risk of cyber threats, protecting not only the devices themselves but also the sensitive data they collect and process.
Visit edge device security to learn more about how MicroAI provides AI-enabled edge device security.
