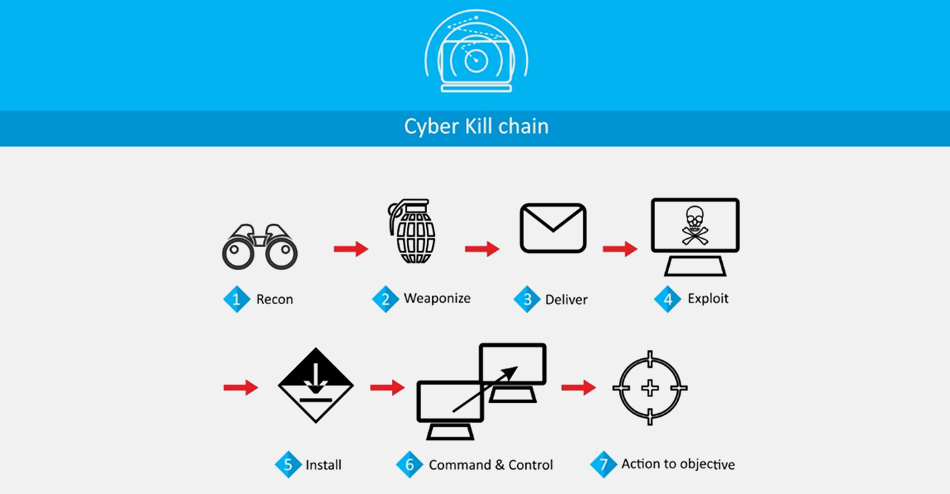
The cybersecurity kill chain is the framework that outlines the stages of a cyberattack, from initial reconnaissance to the ultimate exfiltration or destruction of data. Developed by Lockheed Martin in 2011, the kill chain breaks down an attacker’s methodology into discrete phases, helping security professionals better identify, defend against, and mitigate cyberattacks. The chain is typically broken down into seven stages:
- Reconnaissance
- Weaponization
- Delivery
- Exploitation
- Installation
- Command and Control
- Actions on Objectives
Each stage in the chain represents a potential entry point for an AI-enabled cybersecurity solution to either prevent or mitigate an attack.
Reconnaissance: The Information Gathering Phase
The first stage in the kill chain is reconnaissance, where the attacker gathers information about the target. This can include system vulnerabilities, IoT weaknesses, network configurations, and employee information. This is typically done via hacking tools that automatically collect technical information about targeted devices or networks.
AI-Enabled Protective Measures:
- AI-powered threat intelligence tools scan for suspicious activity on networks, machine, edge devices, and processes.
- Machine learning models detect unusual patterns and behaviors indicating pre-attack reconnaissance.
- Predictive analytics flag high-risk IPs and domains.
Weaponization: Creating the Attack
During weaponization, the attacker creates a malicious payload that will exploit identified vulnerabilities. This could involve crafting a virus, Trojan horse, or other malware, packaged in a way to be deployed during the next phase of the kill chain.
AI-Enabled Protective Measures:
- AI-driven sandboxing environments analyze malicious payloads in real time.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools scan phishing emails and documents for malicious intent.
- AI detects polymorphic malware that changes signatures to evade detection.
Delivery: Deploying the Attack
Delivery is the point in the cybersecurity kill chain where the attacker delivers the weaponized payload to the target. This could happen through email attachments (phishing), edge device penetration points, or network vulnerabilities.
AI-Enabled Protective Measures:
- AI-based email security solutions block phishing and spear-phishing attempts.
- Machine learning algorithms inspect URLs and attachments in real time.
- AI-powered firewalls and IDS/IPS solutions identify abnormal packet flows.
Exploitation: Triggering the Attack
Exploitation occurs when the attacker activates the payload, exploiting a vulnerability in the target system to gain unauthorized access or execute malicious code. At this stage, the attacker typically leverages a zero-day vulnerability (an unknown flaw in the system) or a known exploit.
AI-Enabled Protective Measures:
- AI-driven endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems detect and mitigate exploit attempts.
- AI enhances zero-day vulnerability detection by identifying patterns in exploitation behavior.
- Automated patch management powered by AI reduces exposure to and helps minimize vulnerability.
Installation: Attaining Persistence
Once exploitation has been achieved, the attacker aims to maintain persistence in the system by installing backdoors, rootkits, or other malicious software that allows them to return even after an initial removal attempt.
AI-Enabled Protective Measures:
- AI models detect unauthorized software installations and blocks execution, all in real time.
- Behavioral AI isolates compromised systems before malware spreads to other network components or associated edge devices.
- AI-powered deception technology lures attackers into controlled environments.
Command and Control: Establishing Communication
At this stage of the cyber kill chain, attackers establish a communication channel (C2) between their compromised system and the attacker’s infrastructure. This allows them to issue commands, exfiltrate data, or even deploy additional malware.
AI-Enabled Protective Measures:
- AI-enabled network monitoring tools detect beaconing and unusual outbound traffic.
- AI identifies patterns of communication used by malware for C2 communication.
- Automated threat hunting disables botnet and ransomware command servers.
Actions on Objectives: Achieving the Goal
The final stage in the kill chain is the attacker executing their objective, such as data exfiltration, destruction of data, or other malicious actions. This is the most dangerous part of the kill chain, as it represents the culmination of the attacker’s efforts.
AI-Enabled Protective Measures:
- AI accelerates forensic analysis and post-breach investigation.
- Automated threat containment and rollback mechanisms restore affected systems.
- AI-driven SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) tools coordinate rapid incident response.

Protecting the cybersecurity kill chain now requires integration of AI-enabled counter measures. Through real-time monitoring, proactive alerts and automated responses, organizations can dramatically reduce the chances of a successful cyberattack.
Visit cyber kill chain to learn more about how an AI-enabled cybersecurity solution can protect your network and your edge devices.
